Otoplasty (Prominent Ear Surgery)
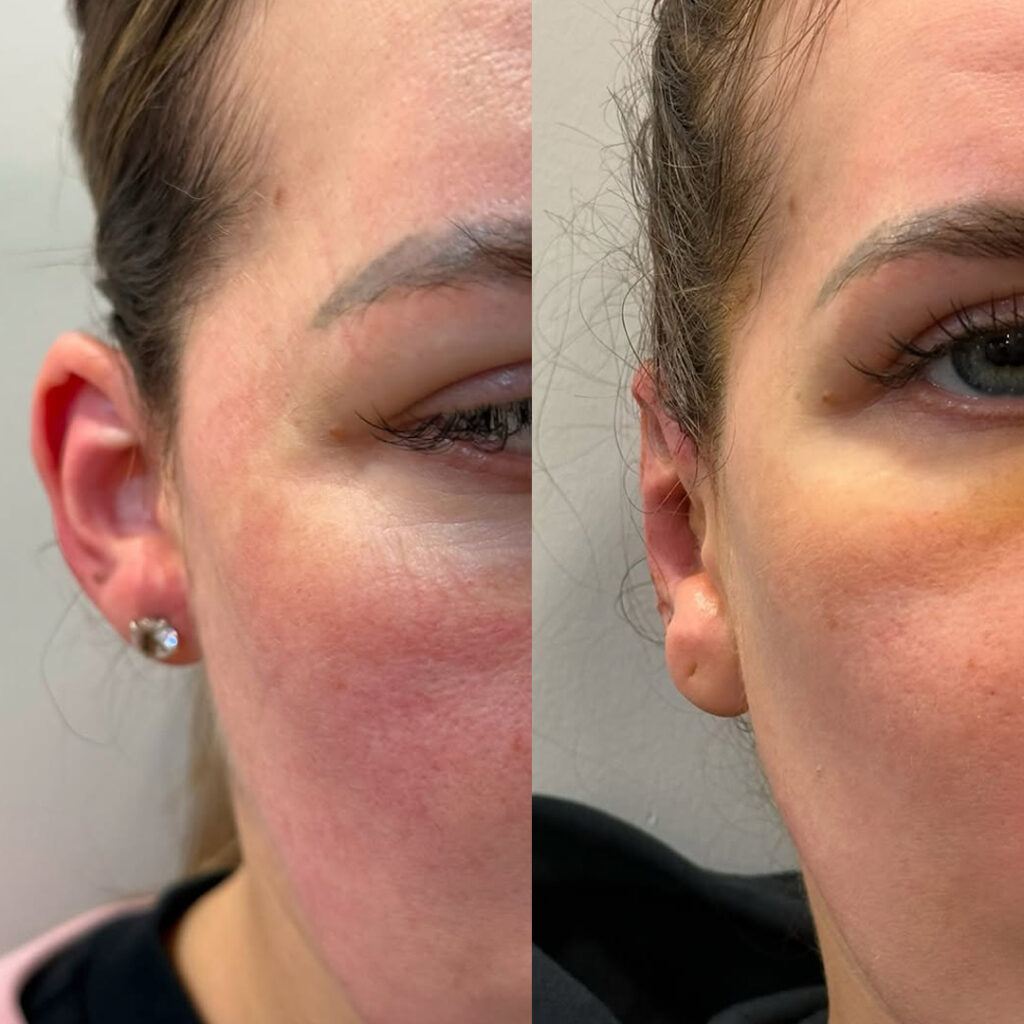
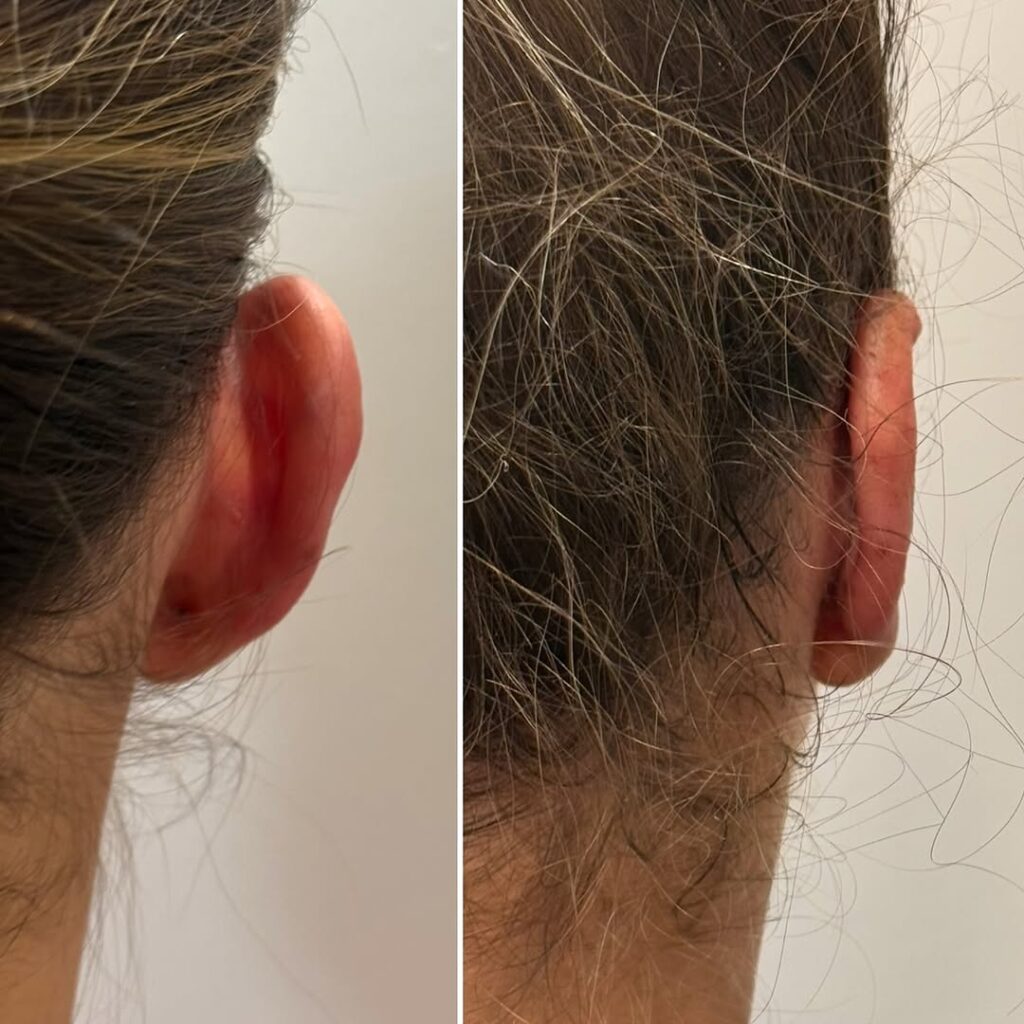
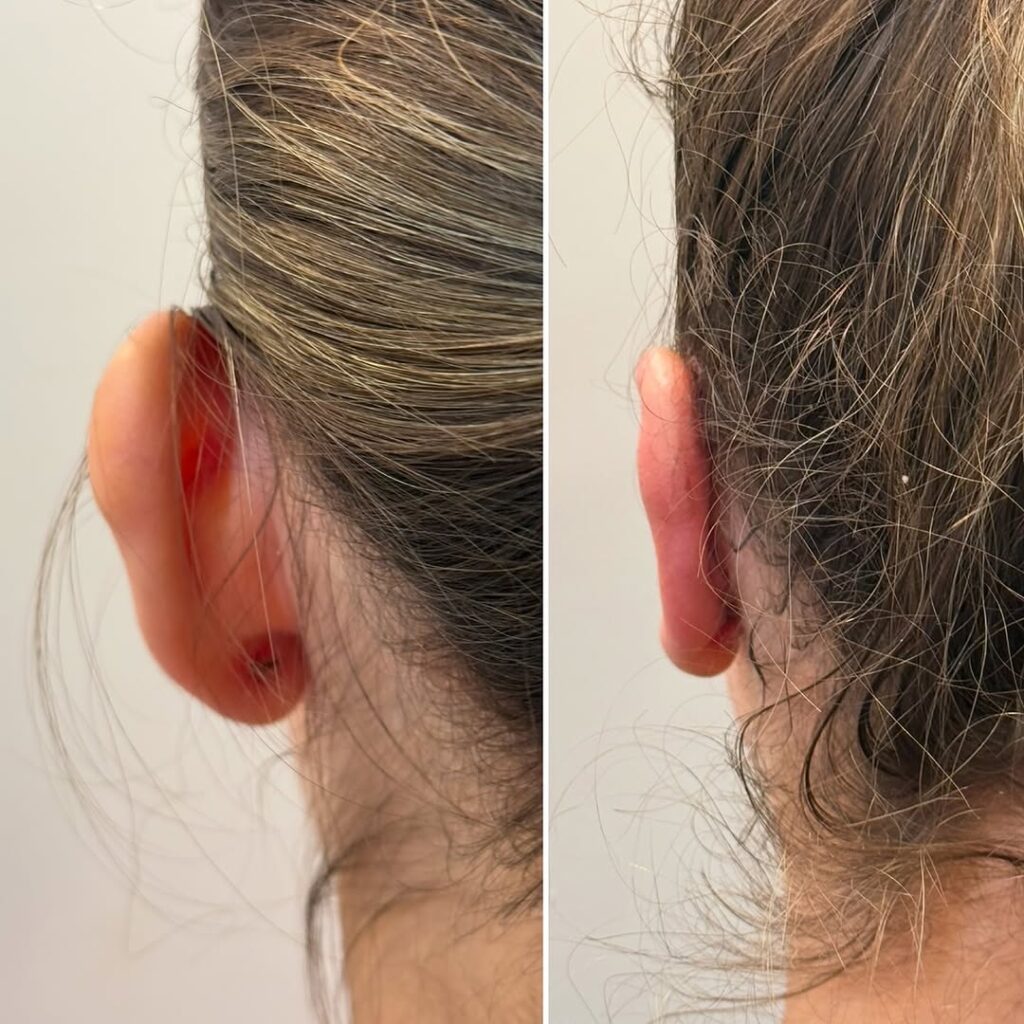
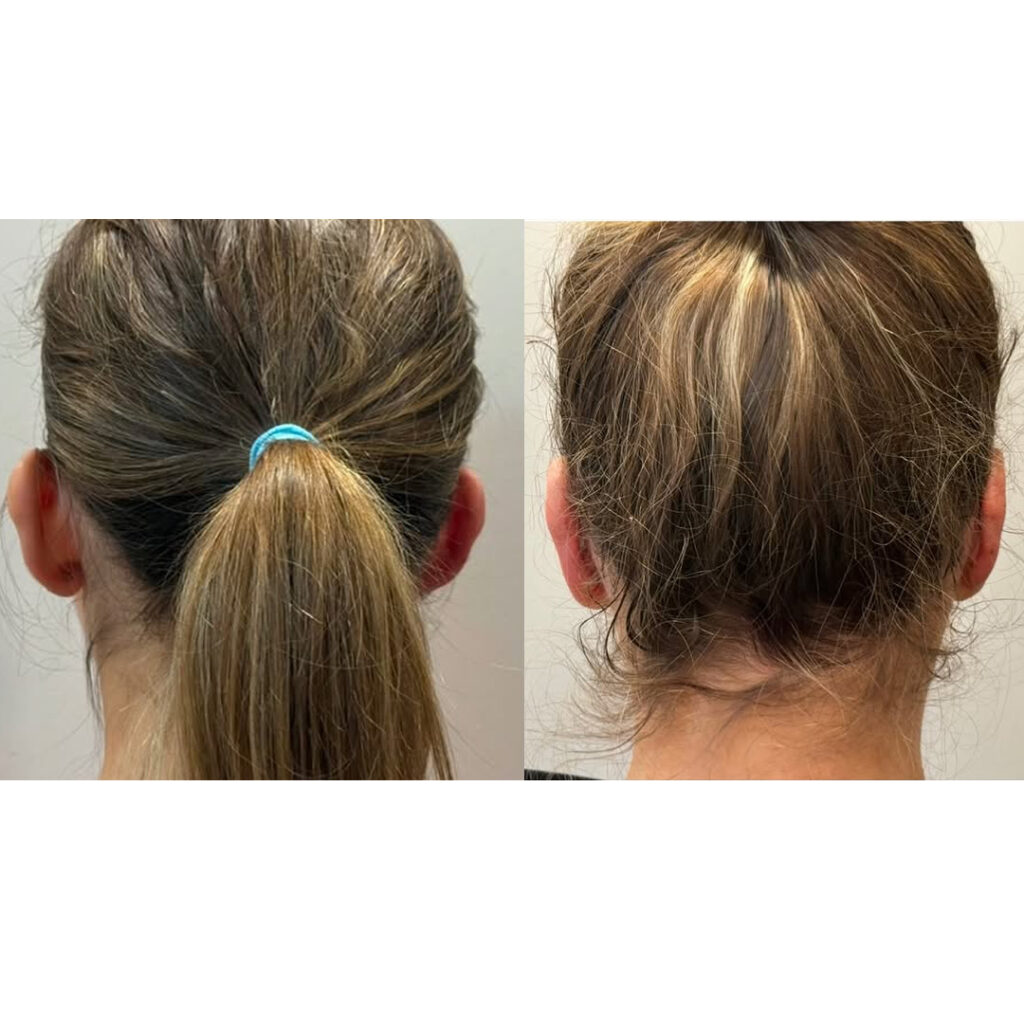
Ear deformities that require plastic surgery can occur for various reasons. One of the most common conditions is prominent (protruding) ears, where the outer ears (auricles) are positioned at a wider angle from the head than normal. In this condition, the ears bend forward excessively and appear overly prominent.
Prominent ears can cause psychological, emotional, and social difficulties, especially in children. These issues may negatively affect self-confidence and social interactions from an early age.
What Is Otoplasty?
Otoplasty is a safe and effective surgical procedure designed to correct the shape, position, or size of the outer ears. This procedure affects only the external ear and has no impact on hearing ability.
Ear development is usually completed by the age of 5–6 years. For this reason, otoplasty is commonly recommended after this age, once ear growth is complete.
Anesthesia and Surgical Technique
In children, otoplasty is typically performed under general anesthesia.
In adolescents and adults, the procedure can usually be done under local anesthesia, which numbs the ear area.
The incision is made behind the ear, ensuring that no visible scars remain after healing.
Ideal Age for Otoplasty
Otoplasty can be performed at any age. However, the most ideal time is before starting school. Children with prominent ears may face teasing or negative comments from peers, which can affect their emotional well-being.
It is important that the procedure is:
Explained to the child in an age-appropriate manner
Performed with the child’s consent and willingness
Preoperative Considerations
As with all surgical procedures:
Aspirin and smoking should be stopped at least 2 weeks before surgery
Blood-thinning medications and supplements should be discontinued during the last week before the operation, as advised by the physician