Gynecomastia (Male Breast Reduction)
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of male breast tissue and is the most common breast condition affecting men. Studies show that at least 30% of men experience gynecomastia at some point in their lives. Although it is a benign condition, gynecomastia can cause psychological distress, social discomfort, anxiety, and fear of breast cancer, leading many patients to seek medical care at an early stage.
Gynecomastia usually develops due to a hormonal imbalance between estrogen and androgen, or an increased estrogen-to-androgen ratio. This imbalance may result from increased estrogen production, decreased androgen levels, or a combination of both.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Gynecomastia
A proper evaluation of gynecomastia requires a comprehensive medical approach, including:
Detailed medical history
Physical and clinical examination
Hormonal and specific blood tests
Imaging studies such as ultrasound or mammography
Tissue sampling (if necessary)
These steps help identify the underlying cause and rule out other possible conditions.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
Treatment for gynecomastia depends on the severity, cause, and individual patient needs. Options may include:
Observation and follow-up in mild cases
Medical (hormonal) treatment
Surgical treatment, which is the most effective solution in advanced or persistent cases
The primary goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms, restore a masculine chest contour, and exclude other etiological factors.
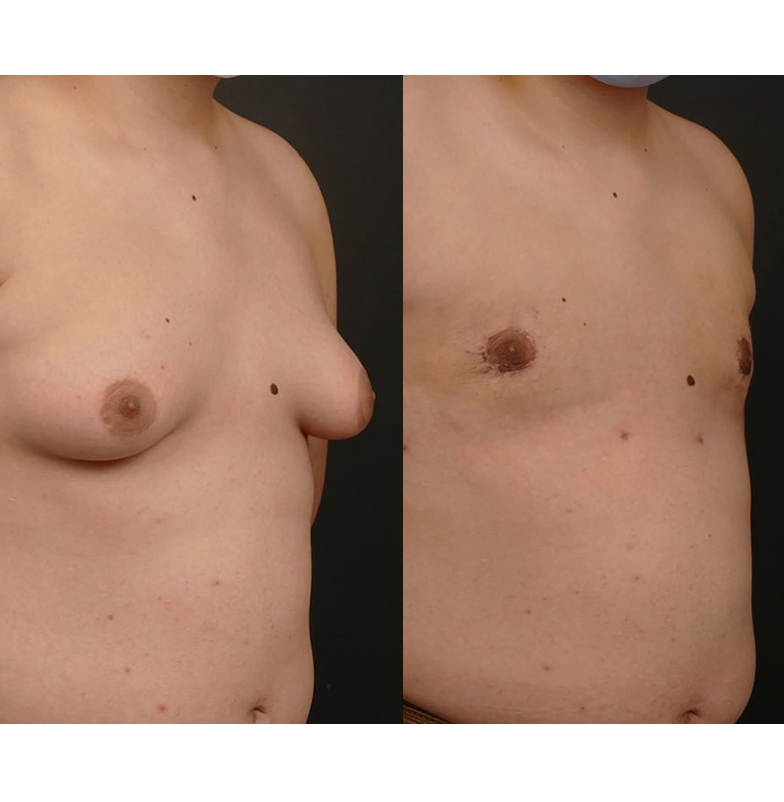
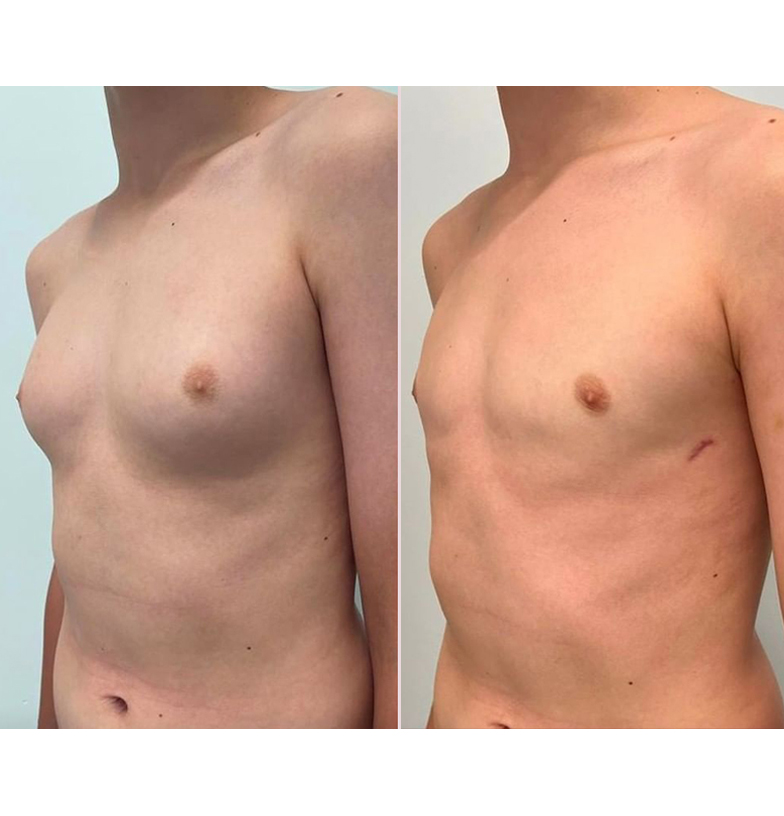
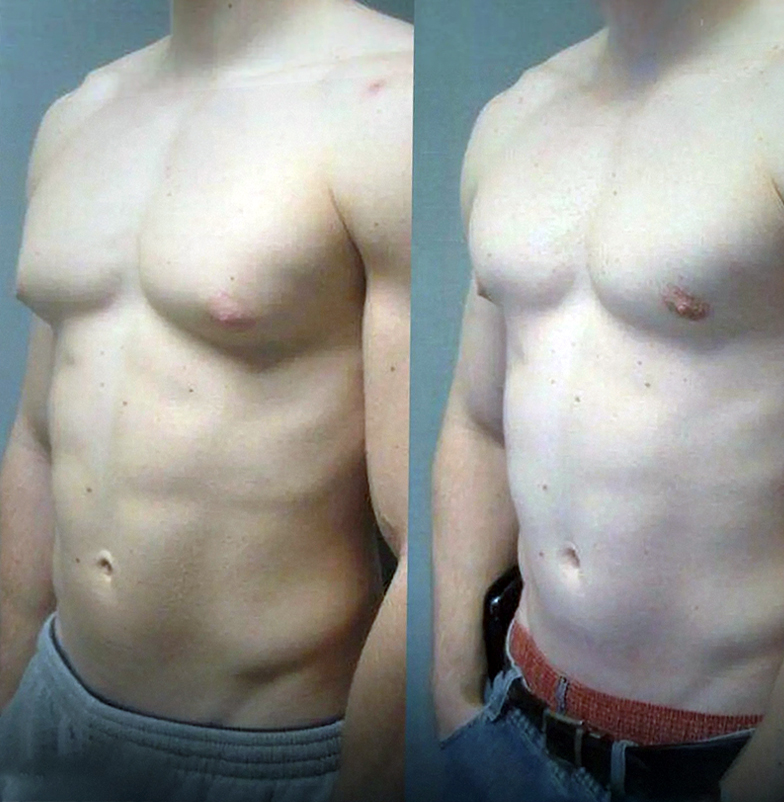
Surgical Treatment of Gynecomastia
Similar to tummy tuck surgery, gynecomastia surgery may involve a combination of liposuction and tissue excision, and in some cases, a skin tightening or lifting procedure. This combined approach allows for a flatter, firmer, and more natural-looking male chest.
Gynecomastia surgery significantly improves body image, self-confidence, and quality of life for many patients.